|
 Arnica
is a genus with about 30 perennial, herbaceous species,
belonging to the sunflower family (Asteraceae). The
genus name Arnica may be derived from the Greek arna,
"lamb," in reference to the soft, hairy leaves. Arnica
is a genus with about 30 perennial, herbaceous species,
belonging to the sunflower family (Asteraceae). The
genus name Arnica may be derived from the Greek arna,
"lamb," in reference to the soft, hairy leaves.
This circumboreal and montane (subalpine) genus occurs
mostly in the temperate regions of western North
America, while two are native to Eurasia (A.
angustifolia and A. montana).
Arnica used to be included in the tribe Senecioneae
because it has a flower or pappus of fine bristles. This
was soon questioned and Nordenstam (1977) placed it
tentatively in tribe Heliantheae s.l. This arrangement
also became uncertain because of the sesquiterpene
lactone chemistry in certain species. Lately Arnica was
placed in an unresolved clade together with Madiinae,
Eupatorieae, Heliantheae s.s. and Pectidinae.
Several species, such as Arnica montana and Arnica
chamissonis, contain helenalin, a sesquiterpene lactone
that is a major ingredient in anti-inflammatory
preparations (used mostly for bruises).
Arnica species are used as food plants by the larvae of
some Lepidoptera species including Bucculatrix arnicella.
Arnica is also known by the names Mountain Tobacco and,
somewhat confusingly, Leopard's bane and Wolfsbane—two
names that it shares with the entirely separate genus
Aconitum.
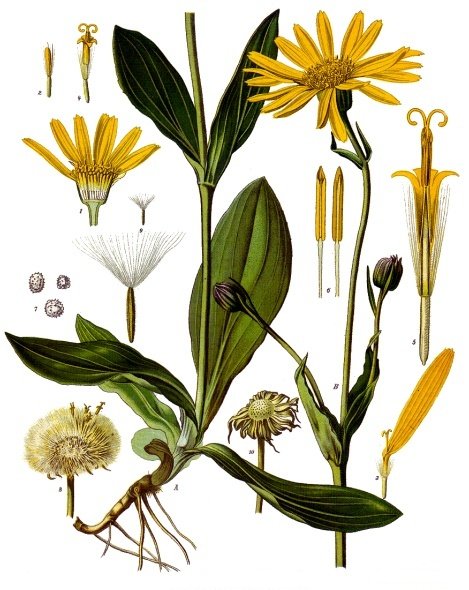
Arnica plants have a deep-rooted,
erect stem that is usually unbranched. Their downy
opposite leaves are borne towards the apex of the stem.
The ovoid, leathery basal leaves are arranged in a
rosette.
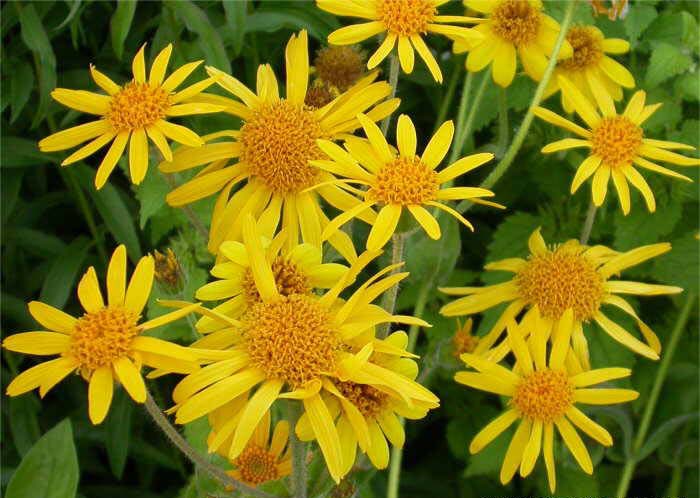
They show large yellow or orange flowers, 6–8 cm wide
with 10–15 long ray florets and numerous disc florets.
The phyllaries (a bract under the flowerhead) has long
spreading hairs Each phyllary is associated with a ray
floret. Species of Arnica, with an involucre (a circle
of bracts arranged surrounding the flower head) arranged
in two rows, have only their outer phyllaries associated
with ray florets. The flowers have a slight aromatic
smell. If taken in the wrong dose it can be very
dangerous.
The seedlike fruit has a pappus of plumose, white or
pale tan bristles. The entire plant has a strong and
distinct pine-sage odor when the leaves of mature plants
are rubbed or bruised.
 Arnica
grows in the mountain woods and pastures of central
Europe and Russia, the Pyrenees and in Northern America
and Canada. The dried flower heads and rhizome are used
herbally and was first used by Swiss mountaineers to
help prevent sore and aching limbs. It has seldom been
used internally because of its irritant effect on the
stomach. Arnica contains the substance: helenalin which
is toxic in large amounts. The roots contain derivatives
of Thymol, which is one of a group of naturally
occurring compounds with strong antimicrobial action (aslo
known as: biocides). Thymol can even reduce bacterial
resistance to common antibiotics such as penicillin. Arnica
grows in the mountain woods and pastures of central
Europe and Russia, the Pyrenees and in Northern America
and Canada. The dried flower heads and rhizome are used
herbally and was first used by Swiss mountaineers to
help prevent sore and aching limbs. It has seldom been
used internally because of its irritant effect on the
stomach. Arnica contains the substance: helenalin which
is toxic in large amounts. The roots contain derivatives
of Thymol, which is one of a group of naturally
occurring compounds with strong antimicrobial action (aslo
known as: biocides). Thymol can even reduce bacterial
resistance to common antibiotics such as penicillin.
Used on unbroken skin to alleviate sprains, muscle pains
and dislocations, it is also said to be helpful when
painted on unbroken chilblains. Applied promptly, it
helps prevent the formation of bruises by stopping the
capillaries from bleeding. It works by stimulating the
activity of white blood cells which process congested
blood, and by dispersing trapped fluids from joints and
muscles and bumped and bruised tissue. It also has
anti-inflammatory and anti-bacterial qualities and it is
these that help to reduce pain and swelling as well as
improving wound healing.
Recent trials involving a team of rugby players and a
group of mothers with young children compared the
efficacy of different bruising treatments.
A variety of bruising treatments
were used including anti-oxidant injections, sports
compresses, painkillers and vitamin K, which is thought
to speed up healing, as well as Arnica cream and
pillules.
In virtually all cases, Arnica was the favoured option:
while the cream was effective in treating bruises and
swelling, the pillules also treat shock and can provide
relief faster as there is no need for it to be absorbed
through the skin.
Arnica is often taken alongside Vitamin C and
bioflavonoids, as both of these further boost the
capillaries to withstand knocks.
Although Arnica may be an
historical remedy, modern science has showed that the
role it plays doesn't just stop with reducing bruises.
Increasing evidence suggests that it also may help the
body recover from surgery, toothache and even
childbirth! Research on dental patients showed that
arnica helped to control pain and bleeding after
treatment.
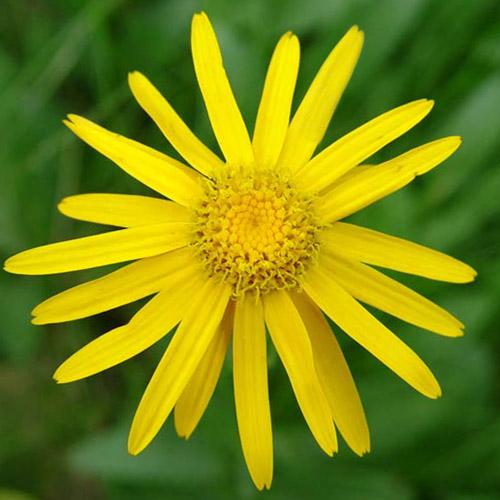
Arnica montana
The species Arnica montana, native
to Europe, has long been used medicinally.
Arnica montana has been used
medicinally for centuries. Arnica is used in liniment
and ointment preparations used for strains, sprains, and
bruises. Commercial Arnica preparations are frequently
used by professional athletes. According to The Memorial
Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, clinical trials "suggest
benefits of arnica for osteoarthritis and reduction in
postoperative swelling and pain."
 Arnica
is used as a topical herbal preparation as well as a
homeopathic remedy. As a herbal remedy for use
externally, arnica is a counter-irritant,
anti-microbial, anti-inflammatory, antiseptic,
anti-rheumatic, anti-neuralgic and anti-oedema medicine. Arnica
is used as a topical herbal preparation as well as a
homeopathic remedy. As a herbal remedy for use
externally, arnica is a counter-irritant,
anti-microbial, anti-inflammatory, antiseptic,
anti-rheumatic, anti-neuralgic and anti-oedema medicine.
Most commonly available as a cream
or ointment, arnica is used for bruises, sprains and
strains, muscle aches, leg and joint aches, rheumatic
pain, inflammation from sports injuries, hematomas,
contusions and fracture-related oedema. Considered by
herbalists as one of the primary first aid remedies,
arnica is never taken internally, unless it is a
homoeopathic preparation. Homoeopathic preparations are
used for similar conditions, as well as pre and post
surgery to prevent swelling and other side-effects.
Dosage
Creams and ointments use 20% to 25%
tincture in a water or lanolin base, or a maximum of 15%
arnica oil made from 1 part arnica and 5 parts vegetable
oil.
Arnica contained in a rub or
soothe, such as those combined with MSM or DMSO are
applied directly to the skin. Dosage
instructions on the product label should be followed or,
a homeopath should be consulted.
|